Wondering what the optimal image dimensions, file size, format, and resolution for your WordPress website are?
Optimizing images is crucial for a website’s success. Poorly optimized images can have a negative impact, slowing down your site, compromising user experience, and even hurting search rankings. In contrast, well-optimized images have the opposite effect, boosting site speed, enhancing engagement, and driving overall performance.
In this guide, we’ll walk you through the different types of images used in WordPress, recommended sizes and formats, and best practices for optimizing images without sacrificing quality.
Whether you’re managing blog post visuals, WooCommerce product images, or social media graphics, this guide will help you make informed decisions to enhance performance and engagement on your site.
Let’s get started.
Table of Contents
Key Takeaways
- Optimized images = faster sites – compressed, properly sized images improve page speed, SEO, and user experience.
- Different image types serve unique roles – blog visuals, featured images, logos, WooCommerce products, and social graphics all have specific size needs.
- Follow size & dimension best practices – e.g., blog posts (1200×675 px), product thumbnails (600×600 px), hero images (1920×1080 px).
- Keep file sizes lean – aim for under 200 KB for posts, under 500 KB for headers, and use tools like TinyPNG or ShortPixel to compress.
- Use the right formats – JPEG for photos, PNG for graphics, WebP for modern compression, and SVG for scalable logos/icons.
Types of Images in WordPress – A Guide
WordPress websites use various types of images, each serving a specific purpose in design, branding, and user experience.
From blog post visuals and featured images to WooCommerce product photos and social media graphics, selecting the right image type ensures better engagement and consistency.
In this section, we’ll explore the most common image types used in WordPress and their roles.
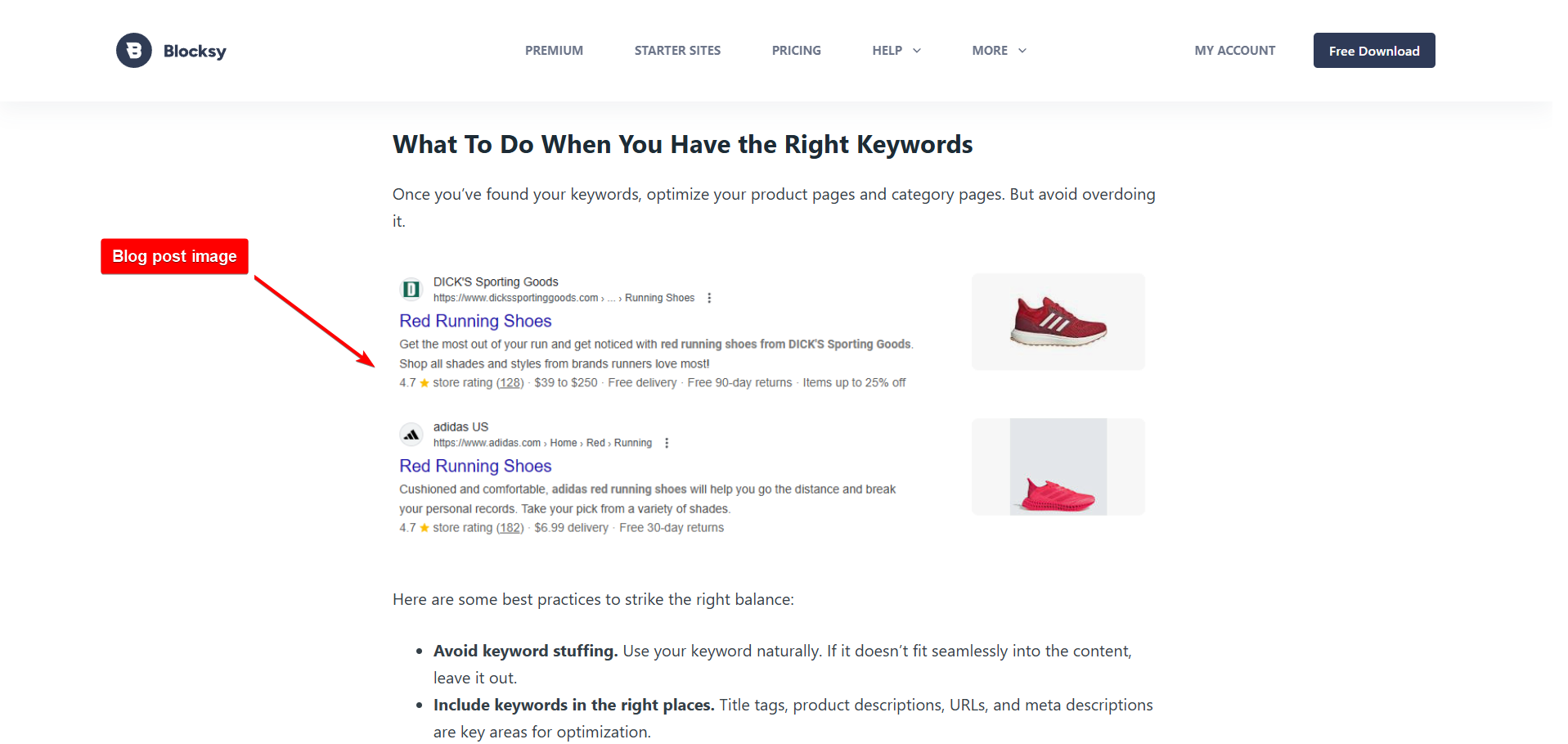
1. Blog Post Images: These images are used to complement written content and make articles more engaging. They can include featured images, inline images, and infographics. These images help convey information more effectively, illustrate key points, and attract readers’ attention.
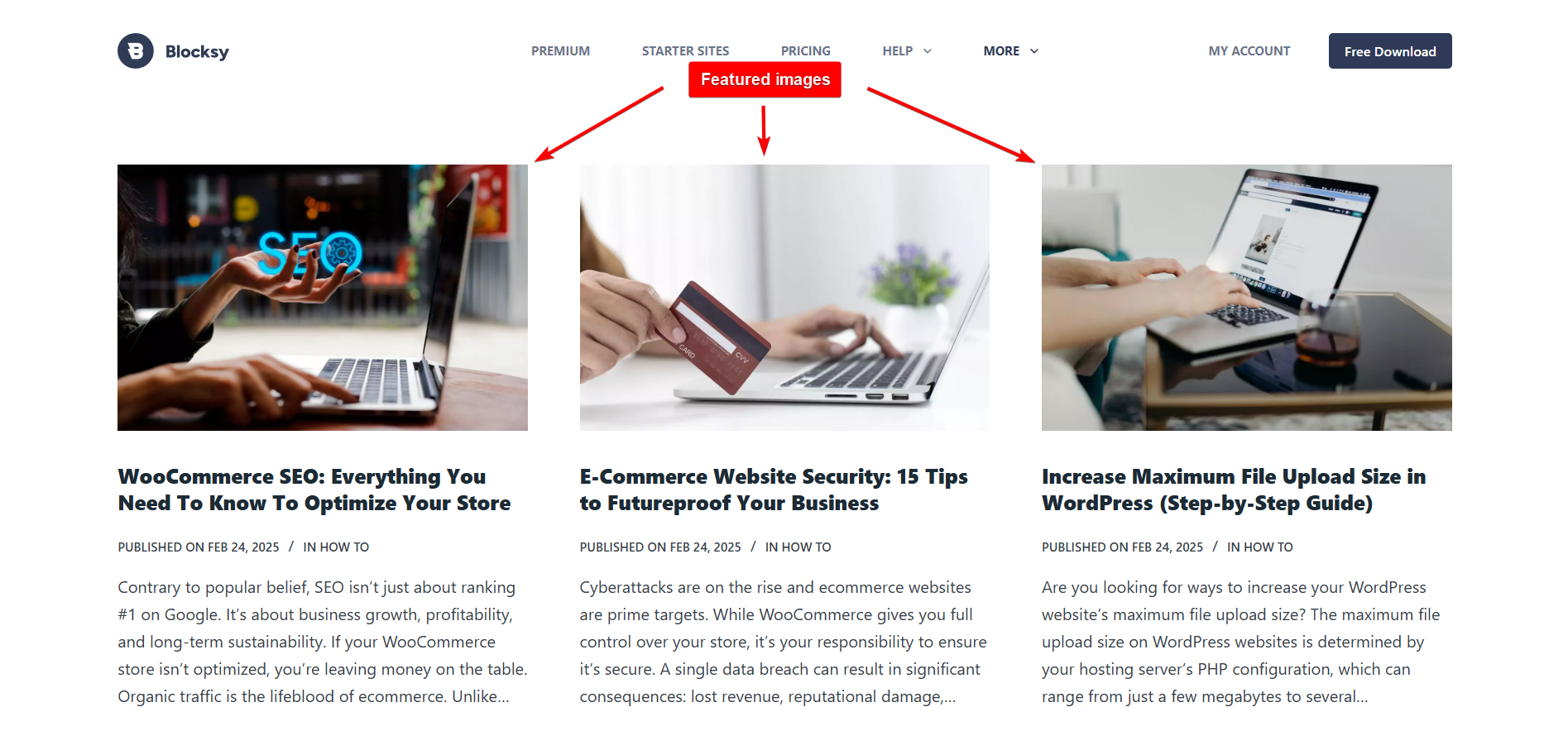
2. Featured Images (Post Thumbnails): Set in blog posts and pages to serve as visual previews when displayed in archives, category pages, or social media shares. They help establish a consistent look across the website and make content more shareable.
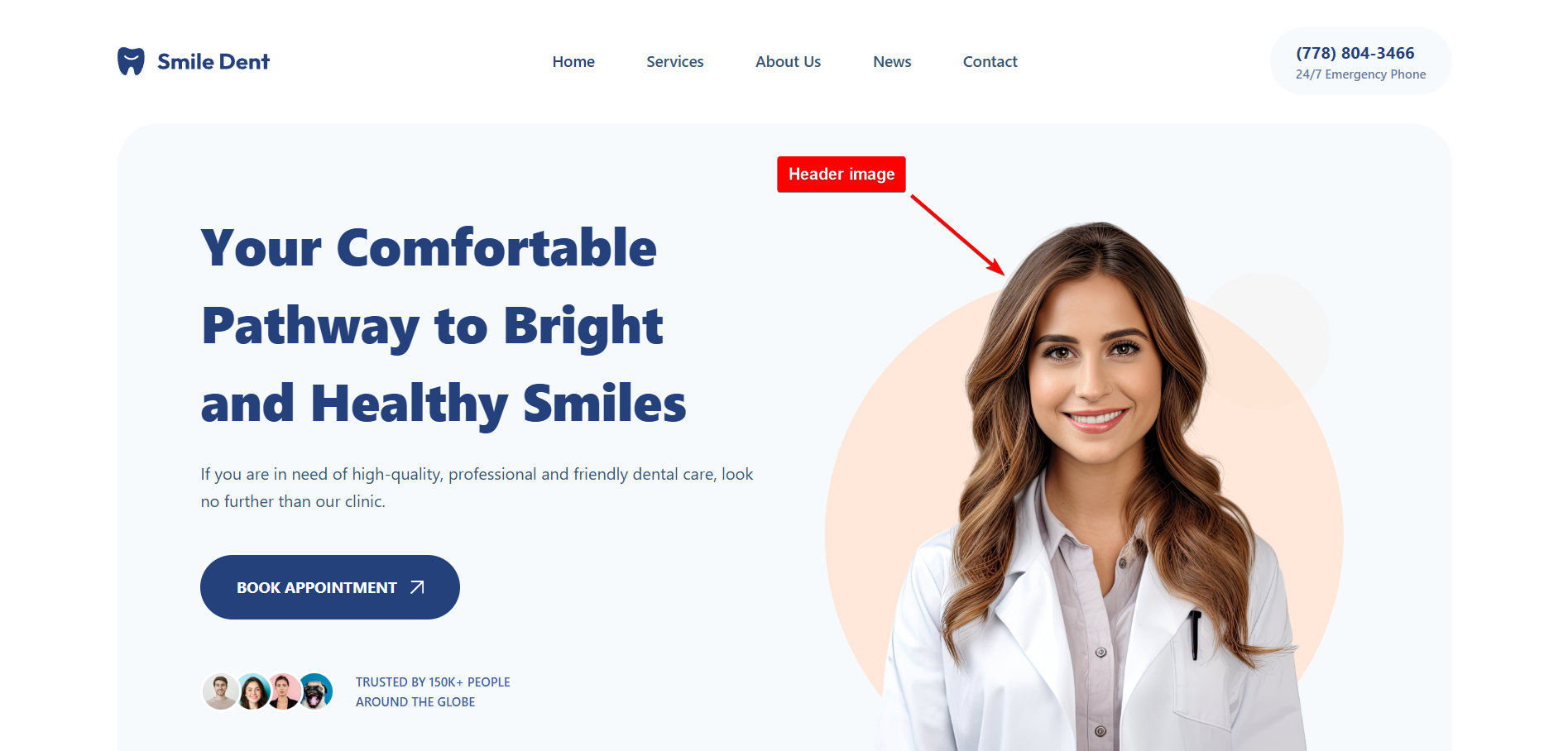
3. Header & Cover Images: Large and full-width visuals used in page headers, hero sections, or banners. They create strong first impressions and set the tone for a website’s branding. These images are commonly used for landing pages, promotional campaigns, or storytelling elements.
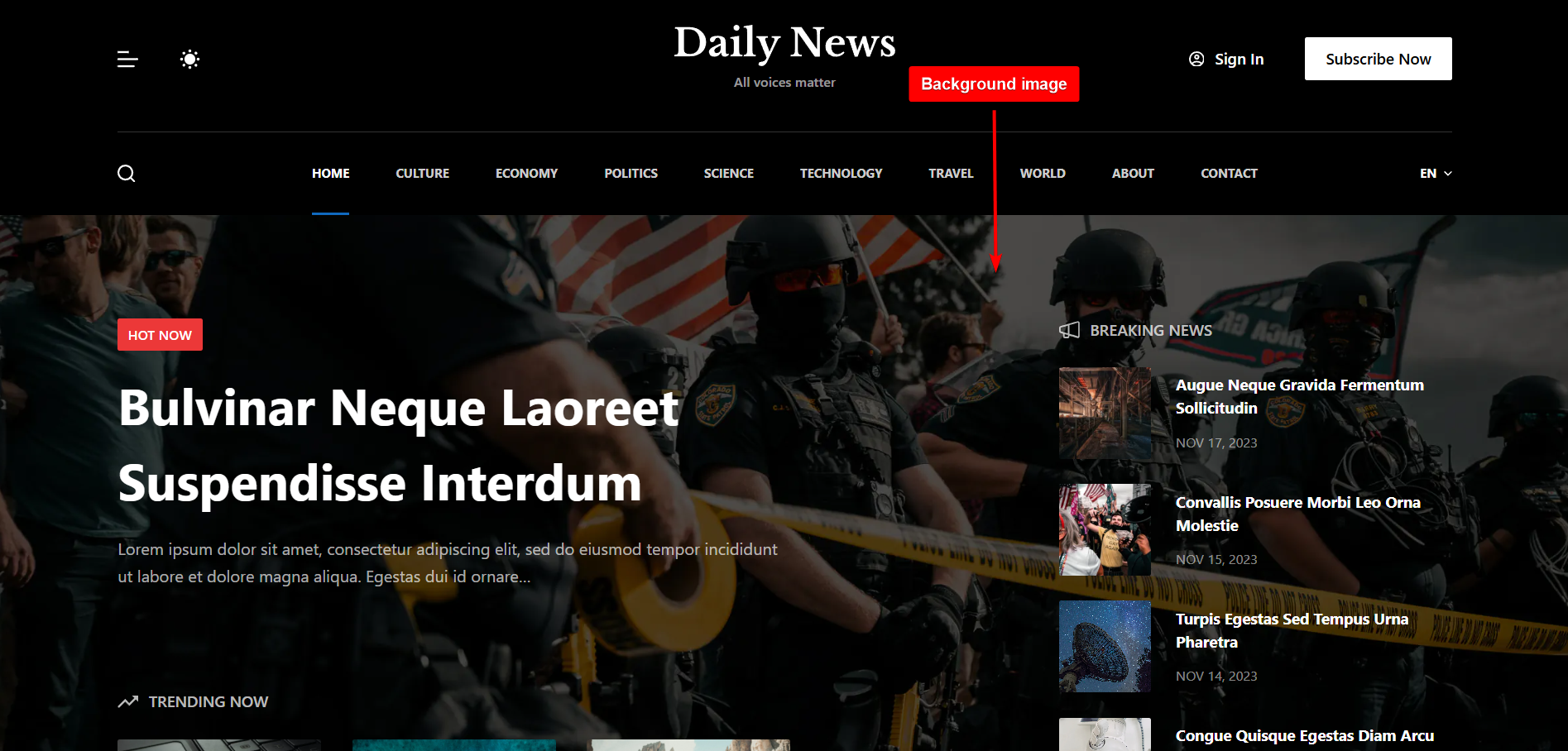
4. Background Images: Used in website sections or full-page designs to add visual depth. They are often utilized in parallax effects, hero sections, or decorative elements to enhance the aesthetic appeal of a site.
5. Logo Images: Logos are an essential part of a brand’s identity and are usually placed in the site header or footer. A well-designed logo ensures brand recognition and consistency across all pages and marketing materials.
6. Thumbnail Images: WordPress automatically generates small previews when media files are uploaded. They are commonly used in post excerpts, galleries, widgets, and related post sections to improve navigation and user experience.
7. Social Media Images: Designed for sharing blog posts, pages, or products across platforms like Facebook, Twitter (X), Instagram, and Pinterest. Optimizing these images for each platform ensures better visibility, engagement, and click-through rates.

8. WooCommerce Product Images: For eCommerce sites using WooCommerce, product images are vital for showcasing items effectively. High-quality images enhance customer trust and increase conversions by providing clear, detailed visuals of products.
What is Image Dimensions, File Size, Formats, & Resolutions?
Understanding the differences between image dimensions, file sizes, formats, and resolutions is essential for optimizing images effectively.
The image’s dimensions affect how images appear on a webpage, the file size influences loading speed, and different formats serve different use cases. Meanwhile, resolution determines image clarity and detail.
This section breaks down these concepts to help you choose the best image settings for your WordPress site.
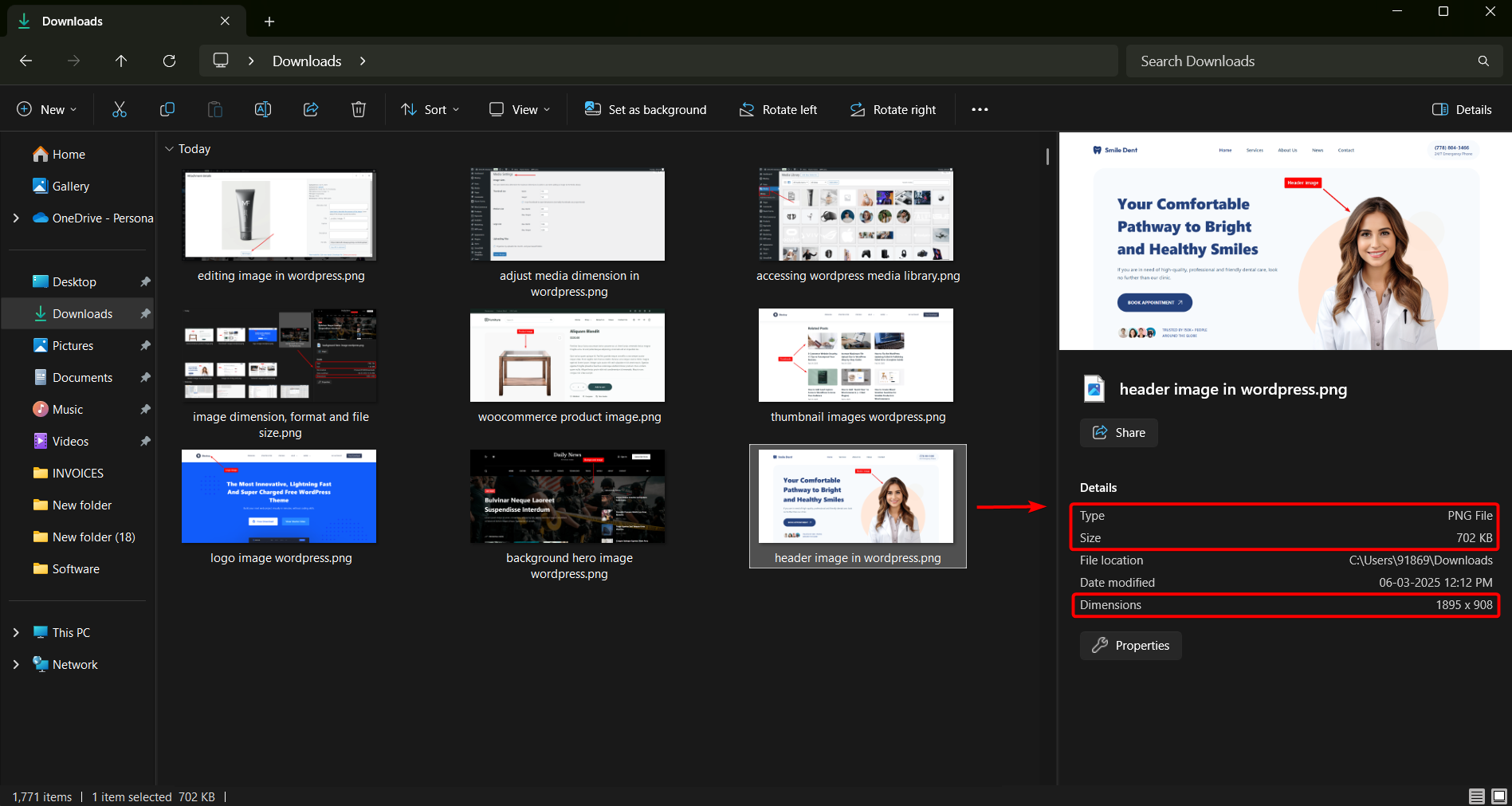
1. Dimensions: Refers to the dimensions of an image in pixels (width×height). It determines how large the image appears on a screen. Larger images take up more space and may slow down website loading times if not optimized properly.
2. File Size: Refers to the amount of storage space an image takes up, usually measured in kilobytes (KB) or megabytes (MB). Larger file sizes can slow down website performance. Compression techniques help reduce file size while maintaining image quality.
3. Formats: Different image formats serve different purposes:
- JPEG (JPG): Best for photographs and detailed images with many colors.
- PNG: Supports transparency and is ideal for logos and graphics.
- GIF: Used for simple animations.
- WebP: A modern format offering high-quality images with smaller file sizes.
- SVG: Scalable vector format used for logos and icons.
4. Resolution: Refers to the amount of detail in an image, often measured in pixels per inch (PPI) or dots per inch (DPI). Higher resolutions are necessary for print-quality images but can be excessive for web use, leading to unnecessarily large file sizes.
Recommended Image Dimensions, File Size, Resolutions, and Formats in WordPress
WordPress itself suggests reducing image dimensions (e.g. hero banners 1920×1080, post images 1200×800) and claims you can often cut file sizes by 50% or more without noticeable quality loss.
WordPress generates multiple image dimensions by default, but optimizing them further can improve page speed and user experience.
In this section, we’ll outline the best image specifications for various use cases, including blog posts, social media, product pages, and more.
1. WordPress Image Dimensions
Default Image Dimensions
When you upload an image to WordPress, it automatically generates multiple versions of it in different sizes. The default sizes are:
- Thumbnail – 150×150 pixels (cropped square)
- Medium – 300×300 pixels (maximum width and height)
- Medium Large – 768 pixels wide (height is auto-scaled)
- Large – 1024×1024 pixels (maximum width and height)
- Full Size – The original image dimensions
Recommended Image Dimensions
Depending on your WordPress theme and site needs, you may need additional image dimensions for specific areas of your website.
Blog Post Images:
- Single-column layout – 1200×675 pixels
- Two-column layout – 680×382 pixels
Featured Images (Post Thumbnails):
- Wide/rectangular images – 1200×687 pixels
- Square images – 600×600 pixels
Social Media Sharing:
- Facebook & X (Twitter) OpenGraph images – 1200×675 pixels
- Pinterest: 1000×1500 pixels
- Instagram: 1080×1080 pixels (square) or 1080×1350 pixels (portrait)
Website Logo:
- 300×200 pixels (varies by theme)
Hero/Header Images:
- Full-width banners – 1920×1080 pixels
WooCommerce Product Images:
- Product thumbnails – 600×600 pixels
- Catalog images – 800×800 pixels
- Full-size product images – 1000×1000 pixels or larger
You can adjust these sizes in Settings → Media in your WordPress dashboard.
2. WordPress Image File Size
Default File Sizes
WordPress itself doesn’t have a fixed file size limit, but your hosting provider does. The typical upload limits are between 2-10MB for shared hosting and 50-100MB for managed WordPress hosting.
Recommended File Sizes
Image file size impacts page speed and performance. Here are general guidelines:
- Thumbnails & Small Icons: Less than 50 KB
- Blog Post Images & Featured Images: 100 KB – 200 KB
- Hero/Header Images & Full-Width Backgrounds: 200 KB – 500 KB
- WooCommerce Product Images: 100 KB – 300 KB
You can use compression tools like TinyPNG, ShortPixel, or Imagify to reduce file sizes without losing quality.
3. WordPress Image Resolutions
Recommended Image Resolutions
WordPress does not enforce a specific resolution (DPI or PPI). However, for best results, try 72 PPI for web images and 150-300 PPI for high-quality prints but unnecessary for web usage.
4. WordPress Image File Formats
WordPress primarily supports JPEG, PNG, and GIF for web graphics and photographs. JPEG offers excellent compression for photos, PNG excels with transparent images and sharp graphics, and GIF works well for simple animations.
SVG and ICO files have more complex support. While not natively supported, plugins like SVG Support and Enable SVG, WebP, and ICO Upload can extend WordPress’s file upload capabilities. These plugins allow safe uploading of SVG files for logos and icons, addressing security concerns through careful script filtering.
For WebP and AVIF formats, conversion plugins like Convert WebP & AVIF provide additional flexibility, enabling you to use these modern, highly compressed image formats even if your WordPress installation does not directly support them.
For security, WordPress blocks executable files (.exe, .bat, .cmd), script files (.php, .js, .html), and compressed formats like .zip or .rar. Always prioritize web-standard formats and leverage plugins to expand your image format options.
How to Access & Edit Images in WordPress
WordPress provides built-in tools to help you manage, edit, and optimize your images without needing external software. Here’s how you can access and edit images directly from your WordPress dashboard.
To access images, log in to your WordPress dashboard and navigate to Media → Library. Here, you can browse all uploaded images, search for specific files, and filter by media type or date.
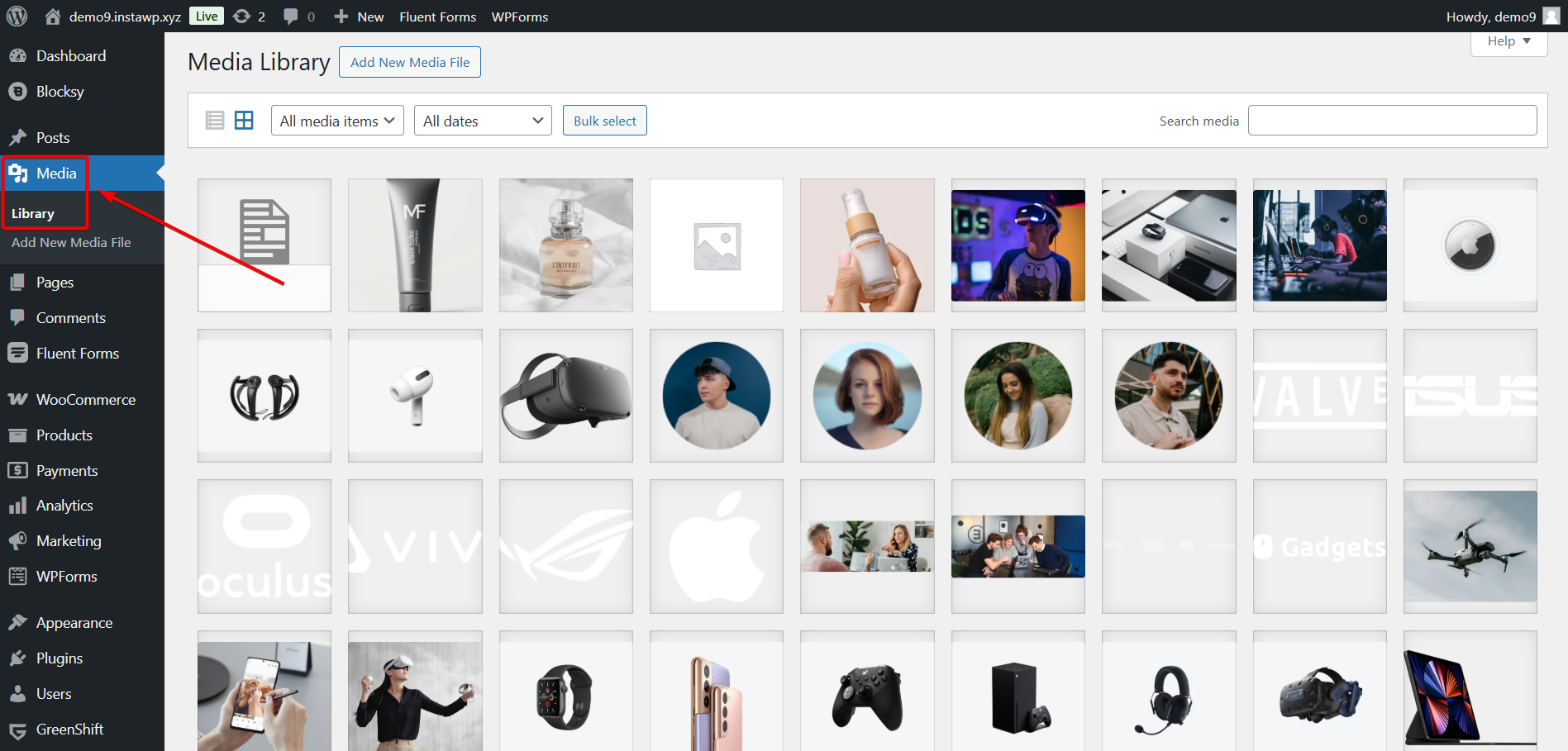
Click Add New Media File to upload images from your device using the drag and drop option or the Select Files button.
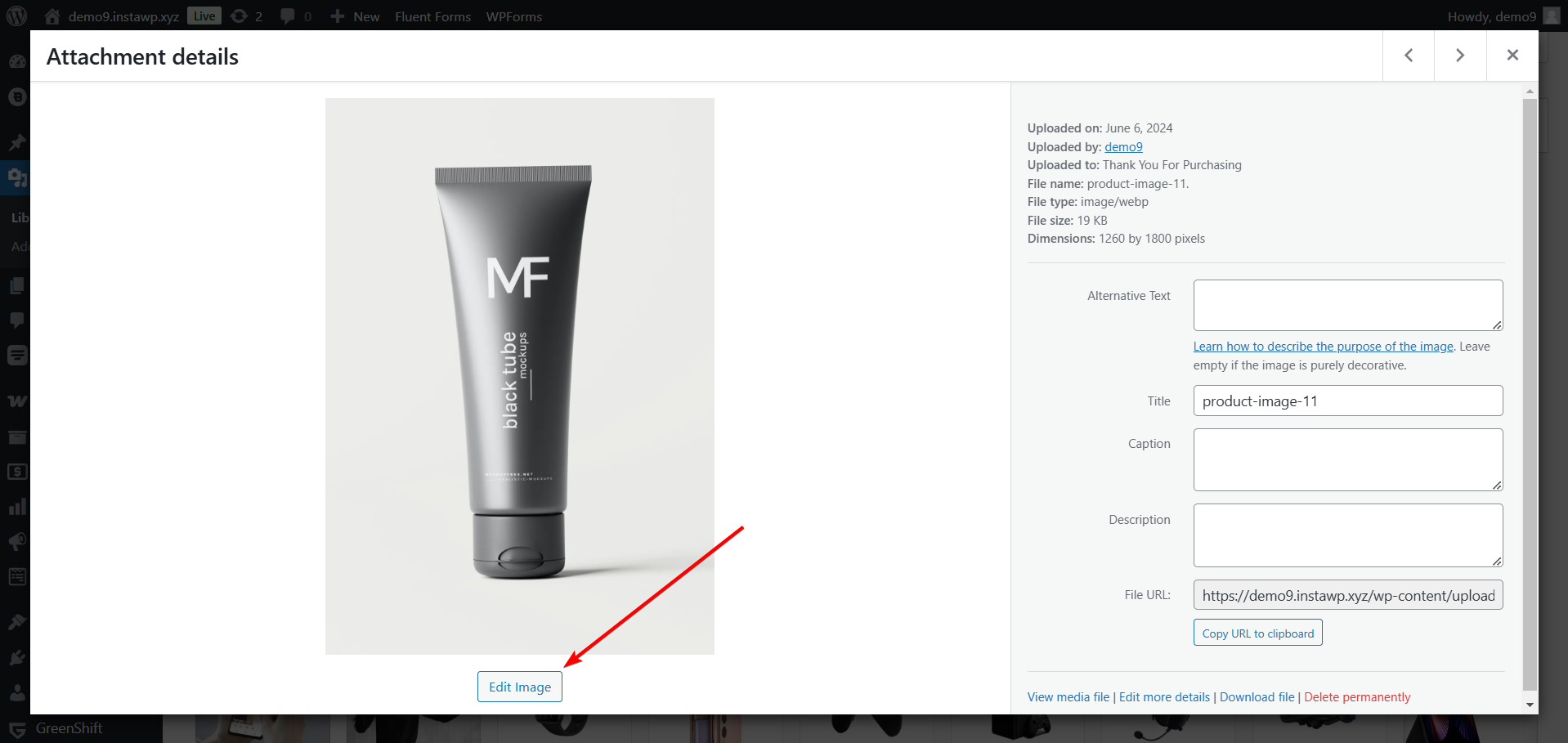
WordPress includes basic image editing features that allow you to crop, rotate, scale, and flip images. In the Media Library, click on an image to open its Attachment Details window and click the Edit Image button.
Your edited image will replace the original file across your site unless you restore the original version.
Plugins for Advanced Image Editing
If you need more advanced editing features, such as applying filters, adding text overlays, or adjusting brightness and contrast, consider using specialized plugins such as ShortPixel, Imagify, and EWWW Image Optimizer.
ShortPixel is a powerful image optimization plugin that automatically compresses images, converts them to WebP, and reduces file sizes without losing quality. It runs in the background, ensuring your website remains fast without requiring manual optimization.
Imagify is another excellent option for image optimization. It offers bulk compression, WebP conversion, and automatic resizing, making it easy to optimize multiple images at once. The plugin provides three compression levels (normal, aggressive, and ultra) so you can balance quality and performance.
EWWW Image Optimizer is a great alternative that automates compression and converts images to WebP. Unlike cloud-based solutions, it processes images directly on your server, giving you full control over optimization settings.
By using these plugins, you can enhance your images while maintaining fast loading speeds, ensuring a smooth experience for your website visitors.
Conclusion
Optimizing images in WordPress is essential for maintaining a fast, visually appealing, and user-friendly website. By understanding different image types, recommended dimensions, file sizes, formats, and resolutions, you can ensure that your site remains efficient without compromising quality.
Using best practices such as compressing images, choosing the right formats, and leveraging WordPress’s built-in tools or optimization plugins will enhance both performance and SEO.
By implementing these strategies, you can improve page speed, boost engagement, and ensure your WordPress website delivers high-quality visuals without unnecessary bloat.
That’s it for this one folks! If you have any questions about WordPress image optimization, please let us know in the comments below.





Hello
Thanks for these best practices for images ! Very helpful !
One question about the “Recommended Image Dimensions” : those dimensions you’re talking about : how can I set them ?
Do I have to import images in these dimensions (for example, if I want a Two-column layout – I import an image with recommended dimensions 680×382 pixels)
Or is there a setting in WordPress (or a plugin) which add those customs dimensions ? (that are not automatically generated by WordPress ) ?