Running an online store means making countless decisions every day, such as what products to promote, which marketing campaigns to invest in, and how to improve your checkout process.
But without proper tracking, all of those decisions are based on guesswork.
That’s where eCommerce tracking comes in. While basic tracking can tell you page views and overall traffic, it doesn’t reveal the full picture of your customers’ journey.
You might know which page gets the most visitors, but not which products people add to their cart or where they drop off in the checkout process. That all falls in the domain of Enhanced eCommerce tracking.
Enhanced eCommerce tracking through Google Analytics gives store owners and marketers a deeper look at user behavior.
It tracks every step of the shopping experience, helping you identify trends, optimize conversions, and make data-driven decisions. For example, you can see which products are viewed most often, which items are abandoned in carts, and which marketing campaigns are actually driving sales.
In this guide, we’ll cover everything you need to know about Enhanced eCommerce tracking in WooCommerce. By the time you’re done reading, you’ll have a clear roadmap to start tracking your store more effectively and turning those insights into real growth.
What is Enhanced eCommerce Tracking?
Enhanced eCommerce tracking is an advanced way to monitor how users interact with your online store, giving you insights far beyond simple page views or traffic numbers.
While standard analytics can show you how many people visited a page or completed a purchase, Enhanced eCommerce digs deeper into the entire customer journey, from browsing products to adding items to the cart, going through checkout, and completing a transaction.
With Enhanced eCommerce, you can track metrics like product impressions, add-to-cart behavior, checkout steps, transactions, and revenue. This data helps store owners, marketers, and conversion optimizers identify bottlenecks and opportunities.
For instance, if many users view a product but don’t add it to the cart, it might indicate a pricing or presentation issue. If checkout abandonment is high, you can test simpler forms, better payment options, or clearer shipping info.
In short, Enhanced eCommerce tracking turns raw visitor data into actionable insights, allowing you to make data-driven decisions that can boost sales, reduce abandonment, and improve the overall shopping experience
It’s also important to note the difference between Google Analytics 4 (GA4) and Universal Analytics (UA). GA4 is Google’s newest analytics platform, focused on events and user behavior across devices, while Universal Analytics relies more on session-based tracking.
Enhanced eCommerce works with both, but GA4 provides more flexibility, richer insights, and future-proof tracking as Google phases out Universal Analytics..
How to Enable Enhanced eCommerce Tracking in WooCommerce
Setting up Enhanced eCommerce tracking in WooCommerce may seem technical, but it’s actually easier than you think.
Whether you use a beginner-friendly plugin or Google Tag Manager, the goal is the same: capture detailed shopping behavior to make smarter, data-driven decisions.
Option #1: Using a WooCommerce-Compatible Analytics Plugin
For beginners or anyone looking for a straightforward solution, using a WooCommerce-compatible analytics plugin is often the easiest way to enable Enhanced eCommerce tracking.
Plugins handle most of the technical setup for you, so you don’t have to add tracking codes or configure complex data layers manually. This approach is ideal for store owners who want reliable tracking without spending hours on coding.

Two of the most widely used WooCommerce-compatible analytics plugins include:
- Google Site Kit. Google’s official plugin for connecting Analytics, Search Console, and other tools.
- WooCommerce Google Analytics Integration. Specifically designed for WooCommerce stores, it supports Enhanced eCommerce events.
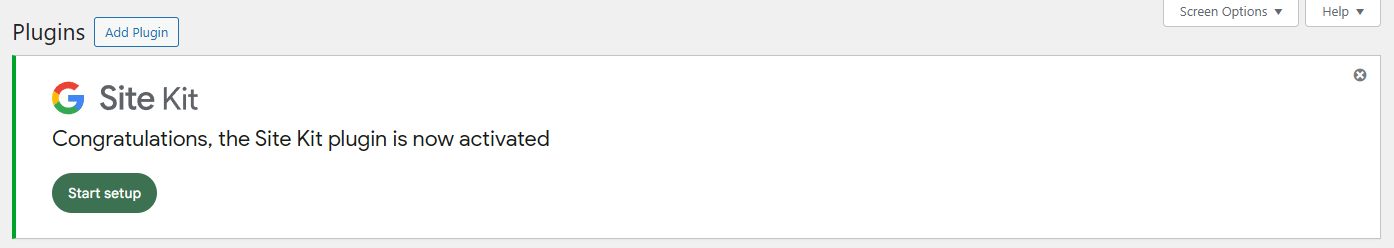
Adding Enhanced eCommerce tracking on your WooCommerce site using a plugin is straightforward. To do this, navigate to Plugins → Add New, search for the Google Site Kit plugin, click Install Now, and Activate.
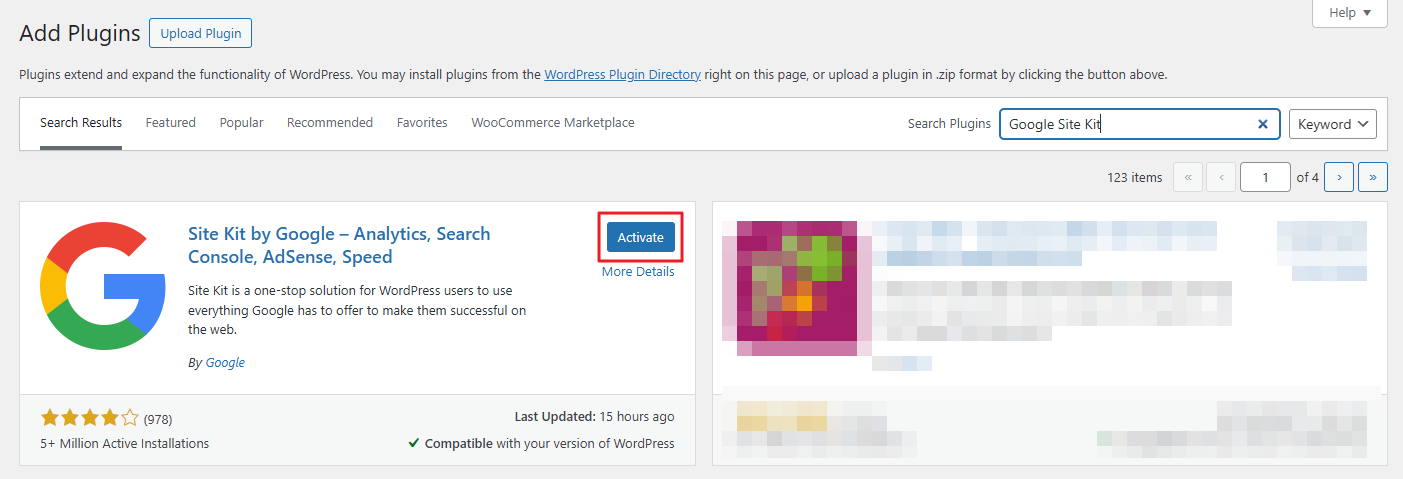
Next, follow the plugin’s setup wizard to link your store with your Google Analytics account. For GA4, ensure you select the correct property during setup.
In the plugin settings, look for an option labeled Enhanced eCommerce or Enable eCommerce Tracking. Toggle it on to start collecting detailed shopping data.
After setup, check that your events are being tracked correctly. You can do this by going to Google Analytics → Realtime → Events and performing test actions in your store, such as adding a product to the cart or completing a test purchase.
Using a plugin is beginner-friendly, reduces the risk of errors, and allows you to start seeing valuable insights immediately.
Once the plugin is active, you can monitor metrics like product impressions, add-to-cart rates, checkout behavior, and transactions.
Option #2: Using Google Tag Manager
For more advanced users or stores with complex tracking needs, Google Tag Manager (GTM) offers a flexible, code-free way to implement Enhanced eCommerce tracking.
GTM allows you to manage all your analytics tags in one place and customize tracking for specific events, campaigns, or user behaviors.
This option makes sense if you run multiple marketing tools, want precise event tracking, or need to implement custom conversions. GTM gives you full control over your data layer and tracking events.

Here’s how you can set up GTM on your WooCommerce site:
- Go to the Google Tag Manager website and create a new account and container for your WooCommerce store.
- Install a plugin like Google Tag Manager for WordPress, or manually insert the GTM container code into your site’s header.
- Ensure your WooCommerce store pushes key data, like product impressions, add-to-cart actions, and transactions, into the GTM data layer. Many GTM plugins handle this automatically.
- In GTM, create tags for GA4 eCommerce events such as view_item, add_to_cart, begin_checkout, and purchase. Test each tag using GTM’s Preview Mode to verify it fires correctly.
Keep in mind, GTM setup can be more complex than using a plugin, and proper testing is crucial. But once configured, it provides flexible, accurate tracking that can scale with your store and marketing needs.
Common Enhanced eCommerce Tracking Issues
Even with proper setup, Enhanced eCommerce tracking can run into issues that affect data accuracy. Understanding common pitfalls (like duplicate transactions or missing revenue) helps ensure your analytics remain reliable and actionable.
Duplicate transactions
One of the most common issues in Enhanced eCommerce tracking is duplicate transactions.
This occurs when the same purchase is recorded multiple times in Google Analytics, inflating revenue and conversion data. It often happens if users refresh the “Thank You” page after completing a purchase or if caching or redirect setups trigger multiple pageviews.
To prevent this, make sure each order has a unique transaction ID, which allows Google Analytics to recognize and ignore repeat submissions.
You can also exclude the order confirmation page from caching plugins to avoid repeated tracking triggers. Finally, always run test purchases after making changes to confirm that duplicates no longer appear.
Missing revenue data
Another common issue with Enhanced eCommerce tracking is missing revenue data, where sales are recorded without the correct revenue figures or not tracked at all.
This can happen if tracking isn’t properly configured on the checkout or “Thank You” page, or if payment gateways redirect users in a way that bypasses your analytics setup.
To fix this, ensure your eCommerce tracking is enabled for both the checkout and order confirmation pages. Double-check that your plugin or GTM setup correctly passes the transaction amount and currency to Google Analytics.
If using GTM, verify that the data layer includes revenue variables. Running test transactions with different payment methods is also a great way to confirm revenue is accurately captured.
GDPR and cookie consent considerations
With privacy regulations like GDPR, Enhanced eCommerce tracking can sometimes fail to collect complete data if users do not consent to cookies or tracking scripts.
This often leads to missing transactions, incomplete customer behavior data, or underreported conversions, which can make analytics misleading. To address this, use a compliant cookie consent solution that clearly asks users to opt in before firing analytics scripts.
Ensure your Google Analytics or GTM setup respects consent signals i.e. it only tracks events after permission is given. You can also implement gradual consent banners that explain the benefits of enabling tracking for a better shopping experience.
In addition to this, test your setup by browsing your store in a consent-free state to confirm data is only collected after approval, keeping your analytics accurate and compliant.
Conflicts with caching or performance plugins
Caching and performance optimization plugins can sometimes interfere with Enhanced eCommerce tracking, causing delays, missing events, or duplicate transactions.
These plugins work by storing pages to serve them faster, but this can prevent Google Analytics or Google Tag Manager from accurately recording dynamic eCommerce events, such as add-to-cart actions or purchases. To prevent issues, exclude critical pages like the checkout and “Thank You” pages from caching.
Check that your optimization plugins, such as minifiers or script defer tools, aren’t blocking analytics scripts. Additionally, use your plugin’s test or preview modes to ensure tracking events fire correctly before going live.
Regularly performing test purchases after plugin updates helps maintain accurate data, ensuring your store analytics remain reliable for decision-making.
Conclusion
Enhanced eCommerce tracking is a powerful tool that helps store owners, marketers, and conversion optimizers understand how customers interact with their WooCommerce stores.
By moving beyond basic tracking, you gain insights into product performance, cart behavior, checkout steps, and revenue, enabling data-driven decisions in place of guesswork.
Getting started doesn’t have to be complicated. You can begin with a beginner-friendly plugin for quick setup or use Google Tag Manager for more advanced, customizable tracking.
Along the way, it’s important to watch out for common issues like duplicate transactions, missing revenue, privacy compliance, and caching conflicts.
Start simple, monitor your data carefully, and refine your setup over time. With consistent tracking and attention to detail, you’ll unlock actionable insights that help improve conversions, optimize marketing efforts, and grow your online store.