As the internet is becoming ubiquitous, more and more people with accessibility needs appear in the digital ecosystem. Website accessibility is an essential feature that doesn’t solely help disabled users but also improves the user experience of every visitor who lands on your site.
According to the World Health Organization’s statistics, there are more than one billion people worldwide who live with some kind of disability, and due to the aging population, this number is growing every year. Thus, targeting the expanding disability market is not only a moral or legal issue anymore but also an important business imperative, which is still largely unrealized.
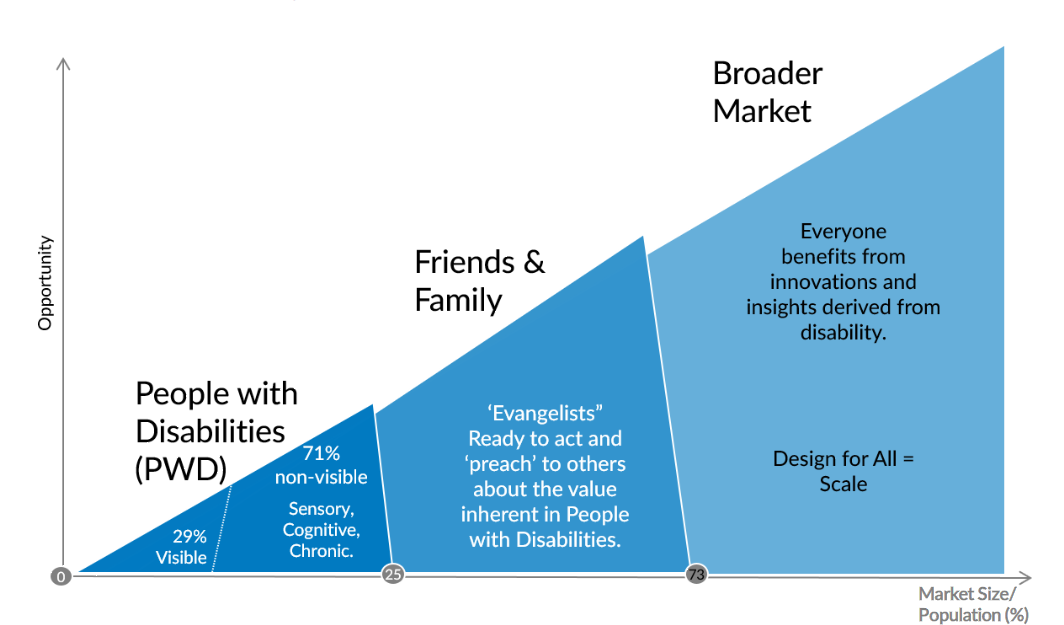
Table of Contents
Key Takeaways
- Accessibility benefits everyone, improving usability and UX across the board.
- 1+ billion people live with disabilities—accessibility is both ethical and smart business.
- Different disabilities require different solutions—design with all users in mind.
- Follow WCAG guidelines for contrast, keyboard access, alt text, and structure.
- Accessibility boosts SEO, reach, and brand trust—not just compliance.
What Is Accessibility?
Accessibility is an overall design objective that aims to make products and services usable for people with permanent or temporary disabilities. Some examples include wheelchair-accessible ramps, Braille keyboards, audio signals at pedestrian crossings, or high-contrast user interfaces.
Digital Accessibility
Digital accessibility is a part of accessibility. It refers to the design and development of websites and applications built with the needs of disabled users in mind, following accessibility guidelines, patterns, and best practices.
Types of Disabilities
Accessibility needs come in many forms, including:
- sensory impairments: the partial or full loss of one of the five senses (sight, hearing, touch, smell, taste)
- physical impairments: the partial or full loss of one or more body system
- mental impairments: various types of mental, cognitive, and psychological dysfunctions
Many disabilities fall into more than one category — for example, vestibular disorders cause both physical and mental symptoms. Some people also have more than one type of disability, such as deaf-blindness.
All in all, disabilities have many intersections that accessible website design needs to take into consideration.
Accessible Website Design and Development
Accessible web design creates digital user experiences that users with different kinds of disabilities can consume, understand, and use without any loss of information and with as little extra effort as possible.
Website accessibility is technically implemented by accessible web development practices that make sure that web browsers, assistive technologies, and other user agents deliver both the content and functionality without any access issues.
Essential accessibility tips for websites:
- Keyboard Navigation: Make all elements accessible with the Tab key; add “skip to content” links.
- High Contrast: Use a 4.5:1 color contrast for text; check with WebAIM.
- Alt Text: Describe images for screen readers.
- Clear Navigation: Structure menus logically and label clearly.
- Readable Fonts: Use at least 16px sans-serif fonts; allow text resizing.
- Captions & Transcripts: Add to all audio/video content.
- Limit Flashing: Avoid flickering and provide animation controls.
- Semantic HTML: Use
<header>,<main>, and ARIA roles. - Regular Testing: Use WAVE and gather user feedback.
Digital Accessibility Needs on the Web (Comparison Table)
The best way to address the digital needs of people with disabilities is using an accessibility-first design approach that starts at the ideation phase and encompasses the entire development workflow — you can even make it part of your DevOps culture.
The following comparison table summarizes the most important things to know about website accessibility:
| Type of Disability | Examples & Symptoms | Assistive Technologies | Accessibility Needs & Solutions |
|---|---|---|---|
| Vision | Blindness, color blindness, low vision | Screen readers, Braille displays, high-contrast mode | – High color contrast for readability – Alt text for images and icons – Adjustable font size for better readability |
| Auditory | Deafness, hearing loss | Closed-captioning software, hearing assistive technology (HATS) | – Closed captions for videos – Transcripts for audio content – Minimized background noise in audio elements |
| Cognitive | Dyslexia, ADHD, autism, memory issues | Text-to-speech software, graphic organizers | – Well-structured content with headings and lists – Reduced distractions – Simplified navigation and error messages |
| Seizure & Vestibular | Epilepsy, vestibular disorders causing dizziness or nausea | Tools to control screen flashing, visual customization options | – Limit flashing animations – Offer controls to disable movement effects – Avoid parallax scrolling |
| Motor | Limited hand function, tremors, paralysis | Adaptive keyboards, voice recognition software | – Clear keyboard navigation – “Skip to content” links – Large clickable areas for easier access |
Web Accessibility Standards and Laws
There are two official resources that can help you implement website accessibility: standards and laws. Laws are mandatory, while web standards are voluntary tools to help ensure compliance and usability.
Website Accessibility Standards
Web standards that discuss digital accessibility implementations are published by the World Wide Web Consortium (W3C).
They are as follows:
- WCAG (Web Content Accessibility Guidelines) 2.0, 2.1, 2.2 (all three are in use: WCAG 2.1 extends 2.0, while WCAG 2.2 extends 2.1). WCAG guidelines cover aspects like color contrast, keyboard navigation, alt text, and screen reader compatibility. Following WCAG 2.1 Level AA, for instance, ensures a solid level of accessibility for most users.
- HTML5 (many assistive technologies understand semantic elements)
- WAI-ARIA (Web Accessibility Initiative – Accessible Rich Internet Applications) for accessibility features website not covered by HTML5
Accessibility Laws and Regulations
While there are many local and regional regulations, the most well-known and frequently quoted accessibility laws are:
- Section 508 of the Rehabilitation Act of 1973 (USA). While Section 508 specifically applies to federal sites, it’s often used as a standard for other organizations to improve digital accessibility and avoid legal risks.
- ADA (Americans with Disabilities Act). The ADA doesn’t specify exact digital guidelines, but it often refers to WCAG as the standard for compliance. Ensuring ADA compliance reduces the risk of accessibility-related lawsuits.
- EAA (European Accessibility Act)
- EN 301 549 (European Standard for Digital Accessibility). EN 301 549 covers a wide range of accessibility needs, from mobile responsiveness to compatibility with assistive technology, ensuring accessible digital content across the EU.
Accessibility Tools and Resources
You can make use of various tools and resources to improve website accessibility, including:
- Accessible color palettes
- Accessibility-ready themes for content management systems such as WordPress
- ARIA best practices
- HTML5 conformance checkers
- Website accessibility testing tools
- Accessibility features of your browser’s developer tools
It’s also recommended that you manually test websites with the tools disabled people typically use, such as screen readers, keyboard navigation, or text-to-speech applications.
However, avoid using accessibility overlays as they can seriously harm website accessibility.
The Impact of Website Accessibility on Your Business
Implementing website accessibility isn’t just a legal or moral responsibility—it brings significant benefits for both users and businesses. Here’s why accessibility matters:
- Reach a Broader Audience: Accessibility allows more people—including those with disabilities—to engage with your site, expanding your reach.
- Enhanced User Experience: Features like clear navigation and readable text improve usability for all visitors.
- SEO Boost: Accessibility practices, such as alt text and semantic HTML, align with SEO, helping improve search rankings.
- Legal Compliance: Meeting accessibility laws reduces the risk of legal issues and demonstrates inclusivity.
- Stronger Brand Loyalty: Accessible websites reflect a socially responsible brand, building trust and loyalty among users.
FAQ
What Is Website Accessibility And Why Does It Matter?
Website accessibility ensures that people with disabilities can perceive, navigate, and interact with online content. It’s not just a legal or moral requirement — it also improves usability for all users and expands your potential audience.
Which Accessibility Standards Should A Website Follow?
The main standards are WCAG 2.0/2.1/2.2, HTML5 semantic structure, and WAI-ARIA for dynamic content. Following WCAG 2.1 Level AA is widely accepted as the baseline for compliance and user inclusion.
How Does Website Accessibility Benefit My Business?
Accessible websites reach more users, improve SEO through clean code and alt text, reduce legal risks, and build brand trust by demonstrating social responsibility and inclusiveness.
Wrapping Up
Implementing website accessibility disabilities takes long-term commitment, accessibility-first design, and continuous testing and evaluation.
It also comes with many advantages — for example, you will:
- support disabled users
- reach a larger audience
- provide better user experience for everyone
- increase business value
- connect with socially conscious customers
- comply with laws and regulations for website accessibility for disabled users
- improve your search engine rankings
To learn more about website accessibility, look into the accessibility checklist of the A11Y Project, check out the success criteria of the WCAG 2.0 guidelines, or generate a WAVE accessibility report for your website.
You can also see how assistive technologies work in practice by giving a try to your device’s built-in accessibility tools, such as Immersive Reader for Microsoft Edge, VoiceOver for iOS and macOS, or TalkBack for Android.
Editor’s note: This article was the first part of our WordPress Accessibility series. It covered website accessibility in general, including the digital accessibility needs of disabled users, website accessibility standards and regulations, tools and resources, and more. Also check out the second part, which discusses WordPress accessibility in detail, and the third part, which looks into the four dos and four don’t of choosing an accessible WordPress theme.